Timing and Navigation in UAVs
Synchronization of UAV Swarms and Testing GPS Error Effects on GNSS Reception
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.14464/ess51265Abstract
Precise timing and precise location information are provided by Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS) and play a crucial role in the positioning, navigation and data acquisition of most Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAV). GNSS functions include the following applications in UAVs: time-stamping and geo-referencing of collected data and images, synchronization of swarm flying and follow-me flights, determination of position and attitude in-flight, flight trajectory by following a pre-defined number of waypoints, mission planning, return home automatically without external control, avoidance of obstacles and geo-fencing.
Some of these critical operations have implications for the safety of the UAV, the surrounding environment and health and safety of people, for example UAVs threatening to bring down aircrafts at airports, which are no-fly zones for UAVs. The appropriate GNSS based function to avoid this is geo-fencing. Another example is obstacle avoidance to prevent collisions and damages both for the UAV and the obstacle, e.g. anything from a window pane, tree, human being, to a power line.
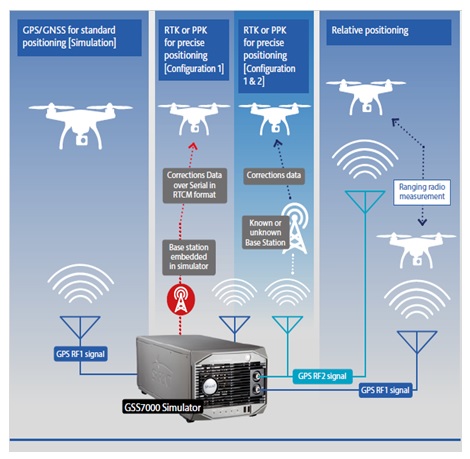
In order to ensure health and safety it is thus important to ensure correct function of the navigation and the timing, under a wide variety of circumstances, and in different signal environments. There can be signal disturbances, such as obscurations by buildings or reflected GNSS signals, called multipath. The performance of timing and navigation based on GPS/GNSS can be tested and verified in a controlled and repeatable way in the laboratory with different types of test equipment. We will give an introduction to a wide range of potential threats to GNSS Positioning, navigation and timing and an overview of different test methods. In addition, we are presenting a method for time synchronization of drones to enable safe swarm and follow flights in UAVs.
Downloads
Published
Issue
Section
License
Copyright for articles published in this journal is retained by the authors. The content is published under a Creative Commons Licence Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0). This permits use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited, and is otherwise in compliance with the licence.


